Trochanteric Bursitis and PT
What is Trochanteric Bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis is a condition where the bursa (a cushioning pad) near the side of the hip becomes inflamed. It causes pain and discomfort on the side of the hip. This makes it difficult to perform daily duties or any of your normal hobbies and activities. The good news is that physical therapy offers effective treatment options to manage trochanteric bursitis symptoms and promote healing. In this blog post, we will explore what trochanteric bursitis is, its symptoms, and how physical therapy can help you feel better.
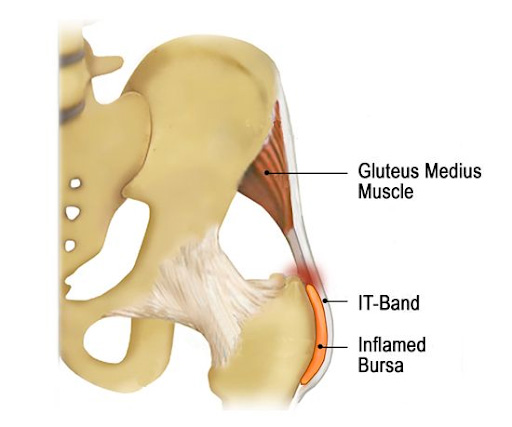
The greater trochanter is the bony bump on the side of your hip. It has muscles and tendons which are located over the bone. Between these muscles, there’s a cushioning pad in between called the trochanteric bursa. The bursa helps to improve lubrication and overall smoothness of tissues that glide over the bone. However, when the bursa becomes inflamed, it leads to pain when contracting the gluteus medius. This is the primary stabilizer of the hip specifically leading to pain with weight bearing over the affected leg.
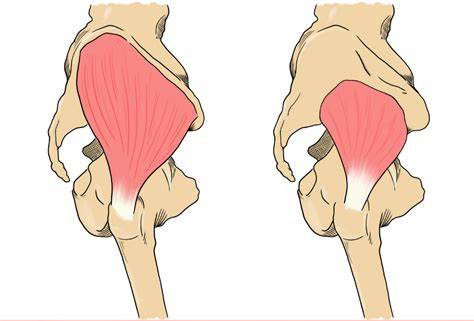
What Causes Bursitis of the Hip?
Trochanteric bursitis can be caused by overuse injuries, muscle imbalances, direct injury, poor body mechanics, or conditions like arthritis. Muscle imbalances in this condition can be caused by weakness of the gluteus medius and minimus, a tendonitis of these muscles, or increased tone/muscle guarding of the TFL. Usually these two issues lead to overcompensation of the IT band to assist with stabilization which puts additional pressure to the bursa, causing it to become inflamed. As pictured above, both the glute med and glute min, respectively, attach to the greater trochanter. A muscular imbalance of these main hip protectors, can lead to an irritation of the bursa leading to pain when walking, running, or jumping. People who do activities involving repetitive hip movements, including runners or cyclists, are more likely to develop this condition if they have surrounding weaknesses.
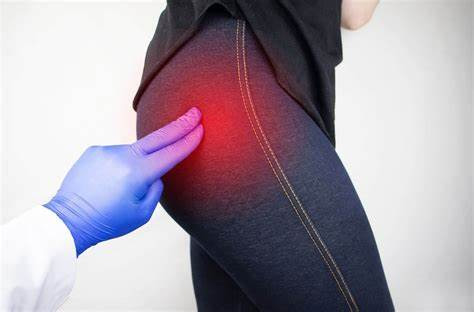
How do I know I have Bursitis?
Common symptoms of trochanteric bursitis include:
- Pain and tenderness on the outer side of the hip.
- Increased pain with activities such as walking, running, or climbing stairs.
- Discomfort when lying on the affected side.
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the hip, especially when moving the leg across or away from the body
- Swelling or warmth around the bony bump on the side of the hip.
Treatment for Hip Bursitis?
Physical therapy is a key part of managing and recovering from trochanteric bursitis. A physical therapist will create a personalized treatment plan based on your needs and goals. The main goals of physical therapy for trochanteric bursitis are:
- Reducing Pain: Initially, the focus is on relieving pain and reducing inflammation using techniques like Winback (TECAR therapy), soft tissue mobilization to the tissues around the affected area, and Dry Needling with electrical stimulation. These methods help ease discomfort and prepare you for later, more active rehabilitation.
- The therapist will use manual therapy techniques such as stretching and soft tissues mobilization along with joint mobility. This helps restore proper hip mechanics, improve flexibility, and reduce tension in surrounding muscles.
- Dry needling with electrical stimulation running through the affected area can help reduce inflammation by increasing opioid levels in the joint, which in turn, drive down factors of inflammation.
- Strengthening Exercises: Weak muscles, such as the buttock muscles and hip abductors, can contribute to muscle imbalances that promote trochanteric bursitis. Your therapist will prescribe specific exercises to strengthen these muscles, improve stability, and promote better movement.
- Addressing Movement Issues: The therapist will assess your movement patterns and identify any biomechanical problems that may be causing or worsening your bursitis. Correcting patterns of running, gait training, or fixing of other loading activities of your lower extremities will be recommended to address any present issues and prevent future flare-ups.
- Educating and Modifying Activities: The therapist will provide guidance on modifying activities or sports that aggravate your condition. They will also teach you about proper body mechanics, posture, and ergonomics to reduce stress on the hip joint during daily activities.
- Gradual Return to Activity: Once pain and inflammation are managed, your therapist will guide you through a progressive rehabilitation program, gradually reintroducing functional activities and exercises to restore strength and mobility.
Closing Thoughts
Trochanteric bursitis can significantly impact your daily life and physical abilities. However, with the help of physical therapy, you can reduce pain, improve mobility, and prevent future issues. By addressing the root causes, strengthening muscles, and promoting better movement, physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing trochanteric bursitis. If you suspect you have trochanteric bursitis, and are looking for a Physical Therapist, come see us at Symmetry Physical Therapy, located in Miami/Brickell downtown area, where we provide an in-depth assessment and treatment strategies so we can help you return to a pain-free lifestyle.
Feel free to give us a call at (305) 331 2277 to schedule an appointment.
